In this tutorial on computer networks, you’re going to learn design issues of data link layer with proper diagrams.
Let’s Get Started, Happy Learning!
Data link layer
The data link layer is the hardware layer, and information at this layer is in the form of frames. The datalink layer is mainly used to define the format of the data. The position of the data link layer is second in the internet model and stays between the network and physical layer as you can see in the following diagram.
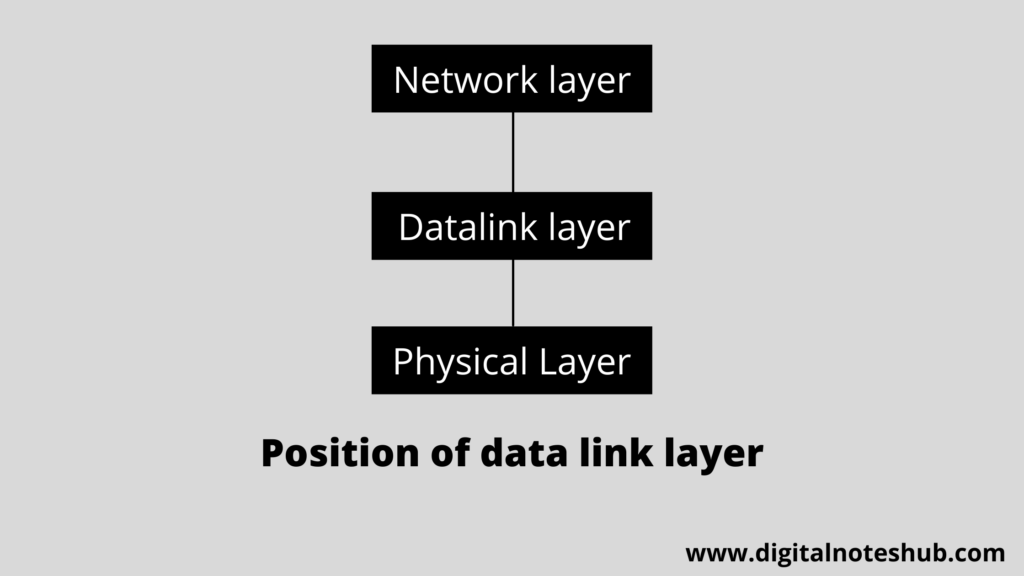
It takes services from the physical layer and provides services to the network layer. The primary function of this layer is data synchronization. The data link layer is further divided into two sub-layers as follows.
- Logical link control sub-layer
- Media access control sub-layer.
Design Issues of Data Link Layer
The data link layer is supposed to carry out many specified functions. It is responsible for effective data communication between two directly connected transmitting and receiving stations.
The data link layer has to carry out several specific functions and the following are the main design issues of data link layer:
- Data transfer
- Frame synchronization
- Flow control
- Error control
- Addressing
- Link management.
Provide Services to the Network Layer
The data link layer provides a well-defined service interface to the network layer. The principle of services is to transfer data from the network layer on the source machine to the network layer on the destination machine.
The transfer is done through DDL(Dynamic-link layer). The data link layer takes services from the physical layer and provides well-defined services to the network layer.
Datalink layer provides three types of services as follows:
- Unacknowledged connectionless service
- Acknowledged connection service
- Acknowledged connection-oriented service.
Frame Synchronization
Frame synchronization is one form the design issues of data link layer. The source machine sends data in a block called frame to the destination machine. The starting and ending of each frame must be recognized by the destination machine.
For frame recognization, every frame comprises three parts, such as frame header, payload field (contains data packet from the network layer) and trailer.
Flow Control
The source machine should not send a data frame at a fast data rate as compared to the destination machine receiving data rate. When the sender sends the data at a high speed, the slow receiver cannot able to handle it and the frame can lose in such cases.
There are two types of techniques that are used for flow control as follows.
- Rate based flow control
- Feedback based flow control.
Error Control
The errors made in bits during transmission from source to destination machines must be detected and corrected. The data link layer ensures error-free data transmission. For this, two types of error control techniques are used in the data link layer are as follows.
- Error detection techniques
- Error correction techniques
Addressing
Addressing is also one of the design issues of data link layer. On a multipoint line, the identity of the individual machines must be specified while transmitting the data frames. Each frame comprises a header in which the source and destination addresses are placed.
Link Management
The initiation, maintenance and termination of the link between the source and destination is required for the effective exchange of data. The data link layer of the OSI Model handles proper link management of connected devices.
Your Feedback
Have you enjoyed this tutorial on design issues of data link layer? Post your thoughts in the comment section below. Also, try the following tutorials on computer networks.
