In this guide, you will learn about a transmission medium in computer networks and its types with the help of proper examples and suitable diagrams.
Let’s get started, happy learning!
What is Transmission Medium in Computer Networks?
A transmission medium in computer networks is a communication channel between sender and receiver and it is used to transfer data from one network to another.
When two or more computers are interconnected through a medium to exchange messages or information, then the medium is known as a transmission medium in computer networks. The transmission medium is also called transmission media.
The transmission medium is a media between interconnected devices. Different types of transmission media have unique properties and are used for different purposes.
Types of Transmission Medium
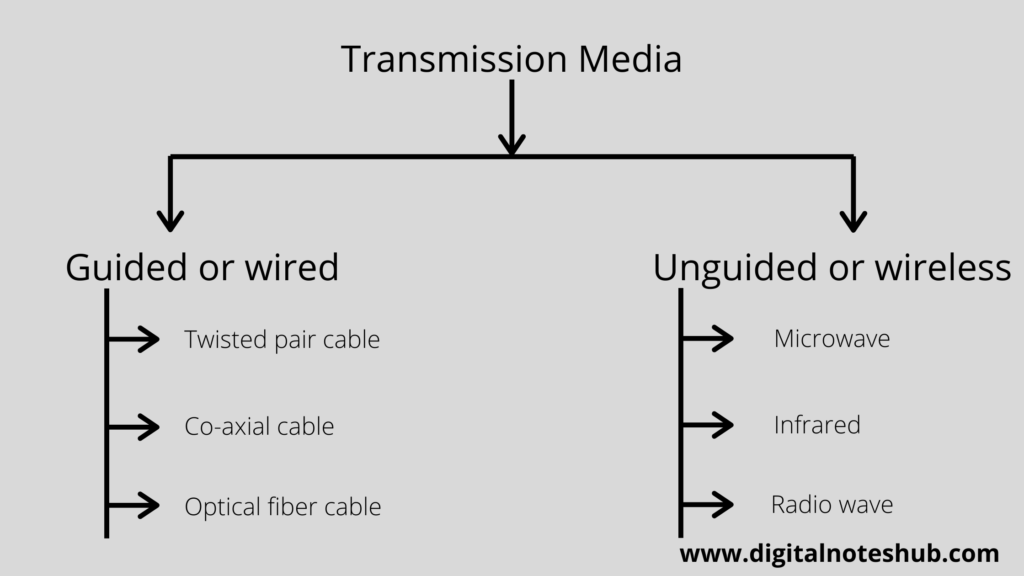
In computer networks, we mainly classify the transmission medium into two types, such as guided and unguided media. The following diagram shows the broad classification of the transmission medium in computer networks.
What is Guided Media?
The media which has a point to point physical connection is called guided media. It is a communication medium that allows data to get guided along with it.
Guided media is also called wired or bounded media. Different types of wires are used to make a physical connection between devices.
Types of Guided Media
Guided media is mainly classified into three types:
- Twisted pair cable,
- Co-axial cable
- Optical fibre.
Twisted Pair Cable
The two wires are typically twisted together in a helix to reduce interference between the two conductors. Twisted pair cables can carry both analog and digital signals. There are two types of twisted pair cables as follows.
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable)
A twisted pair in which two insulated conductors are twisted together is called an unshielded twisted pair cable. UTP cable is very cheap and easy to install.
STP(Shielded Twisted Pair Cable)
It has a metal foil or mesh to cover each pair of insulating conductors. This is also known as the metal shield. The following are the application of an STP cable.
- In telephone lines to carry voice and data channels.
- In the local loop.
- In DSL line.
Co-axial Cable
It comprises two conductors that are separated by a dielectric material. The external conductor is a metallic braid and is used for the purpose of shielding. There are three categories of a co-axial cable, such as RG-11, RG-58 and RG- 59.
The following are the applications of a co-axial cable.
- Analog telephone networks.
- Digital telephone networks.
- Cable TV.
- Digital Transmission.
Optical Fiber Cables
It comprises an inner glass core surrounded by a glass cladding. The cost of fibre optic cable is higher than the twisted pair and co-axial cable. These cables are small and have lightweight. The installation of fibre optical cable is difficult.
The following are the applications of optical fibre cable.
- In the local area networks (LANs).
- Optical fibres are now used in telephone systems.
- These are used in the backbone of networks.
Difference between Twisted pair, Co-axial and Fiber Optics
The following table shows the comparison of three different types of cables that are used in the wired transmission medium.
| Twisted pair | Co-axial | Optical fibre |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission of the signal takes place in the electrical form over metallic conducting wires. | Transmission of signals takes place in the electrical form over the | Signal transmission takes place in an optical form over an optical fibre. |
| Low noise immunity. | Higher noise immunity. | Highest noise immunity. |
| Cheapest | Moderately expensive. | Expensive |
| It has low bandwidth. | It has a moderately high bandwidth. | It has a very high bandwidth. |
Installation of twisted pair cable is easy. | Installation of co-axial cable is fairly easy. | Installation of optical fibre cable is difficult. |
| It can support low data rates. | It can support moderately high data rates. | It can support very high data rates. |
| The short circuit is possible | The short circuit is possible | The short circuit is not possible. |
| Node capacity per segment is Z. | Node capacity per segment is 30 to100. | Node capacity per segment is Z. |
What is Unguided Media?
The medium which provides the transmission of data without a physical connection is called unguided media.
Unguided media provides communication through a wireless medium. It is also called a wireless or unbounded transmission medium in computer networks.
In unguided media, different types of waves are used to transfer data from one network to another through the air.
Types of Unguided Media
The waves such as radio, microwave, and infrared are used in computer networks for unguided transmission media.
Radio Waves
Radio waves have frequencies between 10Khz to 1 gigahertz. The range of the electromagnetic spectrum between 10Khz to 1ghz is called radio frequency. Radio waves can be broadcasted omnidirectional and directionally. Various kinds of antennas are used to broadcast these signals.
- Radio waves include the following types.
- Short waves used in FM radio
- The very high frequency is used in FM radio and TV.
- The ultra-high frequency is used in TV.
Microwaves
Microwaves are basically electromagnetic waves having frequencies between 1 and 300Ghz. These are unidirectional and microwaves propagation is a line-of-sight propagation. The following is the application of microwaves.
- One-to-one communication
- In cellular phones.
- In satellite networks.
- In the wireless local area networks(LANs).
Infrared Waves
The electromagnetic waves having frequencies from 300 GHz to 400 THz are known as infrared waves. These are used for communication between mouse, keyboard, PCs, and printers.
There are two types of infrared media: point to point and broadcasted infrared media.
Difference Between Guided and Unguided Media
The following are the key differences between guided and unguided media in computer networks.
| Guided Media | Unguided Media |
|---|---|
The signal energy is contained and guided within a solid medium. | The signal energy propagates as unguided electromagnetic waves. |
It is used for point-to-point communication. | It is used for radio broadcasting in all directions. |
| Wired transmission media leads to discrete network topologies. | Wireless media leads to continuous network topologies. |
| Additional transmission capacity can be produced by adding more wires. | It is not possible to produce additional capacity in the wireless transmission medium. |
| Installation is costly, time-consuming, and complicated. | Installation needs less time and money. |
| Attenuation depends exponentially on the distance. | For example Twisted pair, co-axial, and fibre optic cables. |
| For example – Twisted pair, co-axial, and fibre optic cables. | For example – Radio, microwave, and infrared waves. |
Additional Notes