In this computer networks tutorial, you’re going to learn about simplex, half duplex and full duplex communication with proper examples and diagrams. If you want to switch to any sub-topic, then you can use the following table of content.
Let’s Get Started, Happy Learning!
Transmission Modes in Computer Networks
Transmission modes in computer networks are used to transfer data between the connected devices. In a network, devices can communicate with each other through transmission modes.
Transmission modes are used to direct the direction of the flow of information and are also called communication modes.
Types of Transmission Modes
There are three types of transmission modes in computer networks as follows
- Simplex Communication Mode
- Half-duplex Communication Mode
- Full-duplex Communication Mode
Simplex Communication Mode
In simplex communication mode, the information is communicated in only one direction. There is only one transmitter and one receiver, hence the system is unidirectional. The following are examples of simplex communication mode.
- Keyboard and Traditional Monitors.
- Radio Systems.
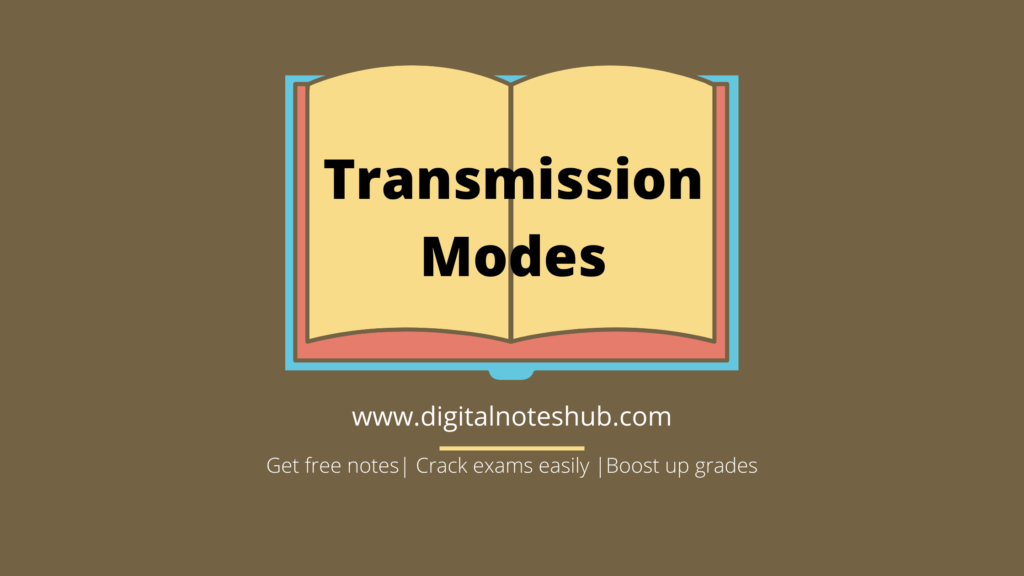
These devices can only transmit the data and cannot receive it. The following diagram shows the simplex communication mode between two connected devices A and B.
As you can see in the following diagram, A is working as a sender and B as a receiver. Hence, the direction of data is from A to B.
Half-duplex Communication Mode
In half-duplex mode, the data flow is bidirectional, but not at the same time. It means both connected devices can transmit and receive data, but not simultaneously. At a time, the device can work either as a transmitter or receiver.
The examples are Transceiver and Walky talky set.
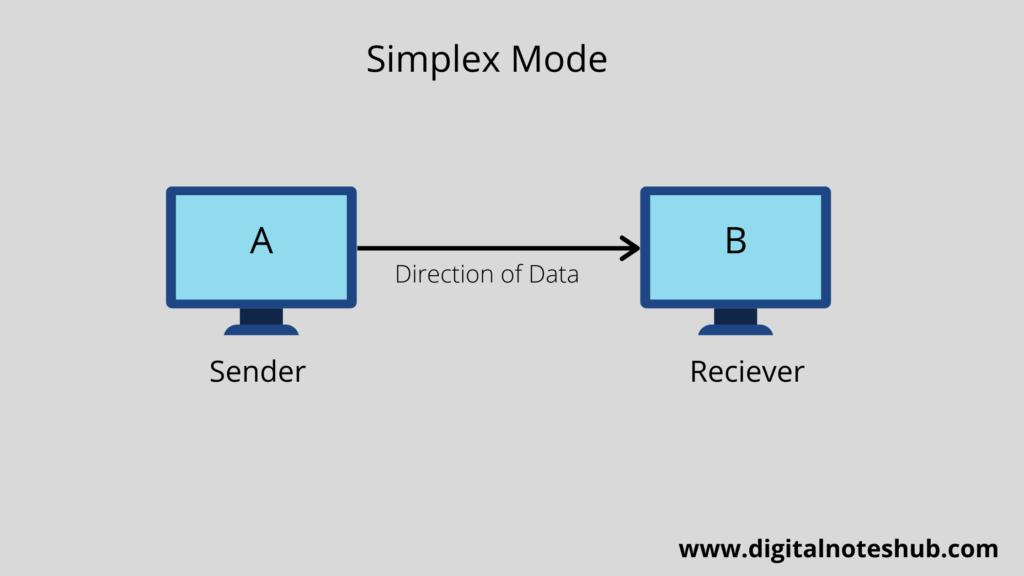
The following diagram shows a half-duplex mode between A And B. At a time T1, A works as a transmitter and B as a receiver. At time T2, A works as receiver and B as a transmitter.
Hence the At time T1 data flows from A to B and at time T2 data flow from B to A.
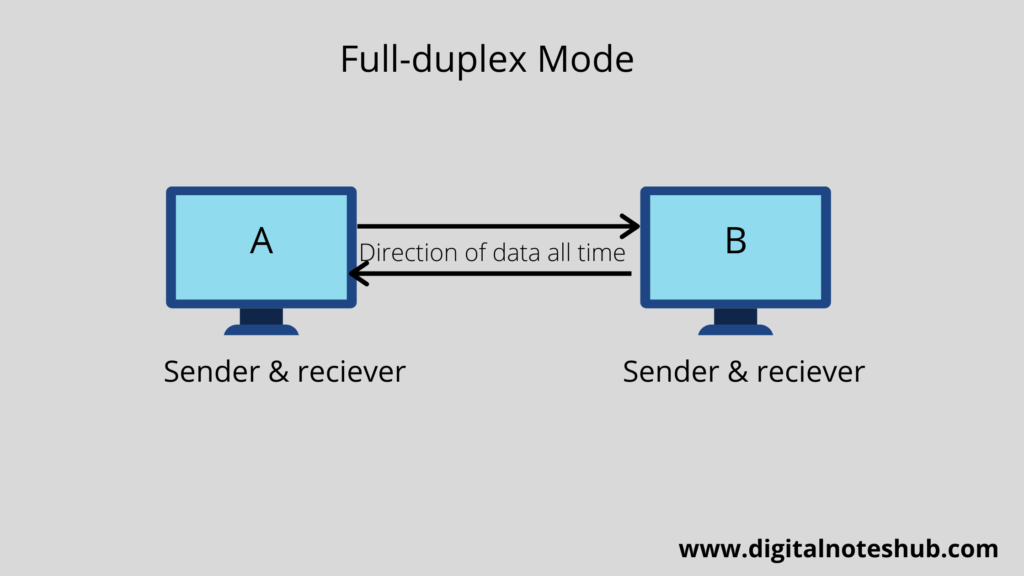
Full duplex Communication Mode
In full-duplex mode, the data flow is bidirectional. It means both connected devices can transmit and receive data simultaneously. The devices can send or receive data at the same time.
An example of a full-duplex mode is the telephone system.
The following diagram shows full-duplex communication between A and B. A and B both work as sender or receiver. And data flow is also from both directions.
Difference Between Simplex, Half duplex and Full duplex Communication
The following table shows the differences between the three communication modes.
| Simplex | Half-duplex | Full-duplex |
|---|---|---|
| The direction of data is only in one direction. | The direction of data is bidirectional, but not at the same time. | The direction of data is bidirectional at the same time |
The sender can send the data but cannot receive the data. | The system can send or receive the data, but not at one time. | The system can send or receive the data simultaneously. |
| It provides less performance than the other two modes. | It provides a high performance than the simplex mode. | It provides a high performance than the other two modes. |
| For example, Traditional keyboard and Monitor. | For example- walky-talky | For example- Telephone |
What are your thoughts?
Have you enjoyed this tutorial on Simplex, half duplex and full duplex? If you have any questions
Additional Notes